Cloudant Integration
Add a Cloudant integration to your backend service
While logged into the IBM Cloud account use the resource list to find your pre installed Cloudant database instance name after your development cluster.
Open the database instance dashboard.
Click on the Service Credentials on the left-hand menu.
You will see the credentials for the database.
Open a terminal window folder/directory called
datamkdir dataTo help create test JSON data we are going to supply a template to the JSON Generator tool, this helps when creating dummy data for testing. Navigate to the following link https://www.json-generator.com/
Replace the default template with the following template (using cut and paste). This will enable a 100 records of test data to be created to represent a products database. Click on the Generate button.
['{{repeat(1, 50)}}',{id: '{{objectId()}}',manufacturer: '{{company().toUpperCase()}}',name: '{{lorem(3, "words")}}',price: '{{floating(10, 1000, 2, "0.00")}}',stock: '{{integer(1, 100)}}'}Copy the generated contents on the right hand side into a file called
inventory.jsonand save it into the same folder. Wrap the array with a docs statement.{"docs": <Add Generated array here>}Save the documents that will be loaded into Cloudant
Download the
dataload.shscript from the Iteration Zero repository - https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ibm-garage-cloud/ibm-garage-iteration-zero/master/terraform/scripts/dataload.shAdd the
usernameandapikeytoCLOUDANT_USERNAMEandCLOUDANT_API_KEYvariables in thedataload.shscript. You can get the credentials from the Cloudant credentials view in the IBM Cloud console.Add
DATABASEvalue to beinventory-<replace with namespace>using the dev namespace/project name you have been using.Save the script, make it executable, and then run it by passing in the filename
chmod +x ./dataload.sh./dataload.sh inventory.jsonThe data from the
inventory.jsonfile will then be used to populate the database, to confirm this on the Dashboard click on Manage menu on the left and then Launch button to see the Cloudant dashboard.Click on the Left icon that looks like a Database and you will see the
inventory-<namespace>database created.Click on the
inventorydatabase, then click Table view.You can see the rows of data
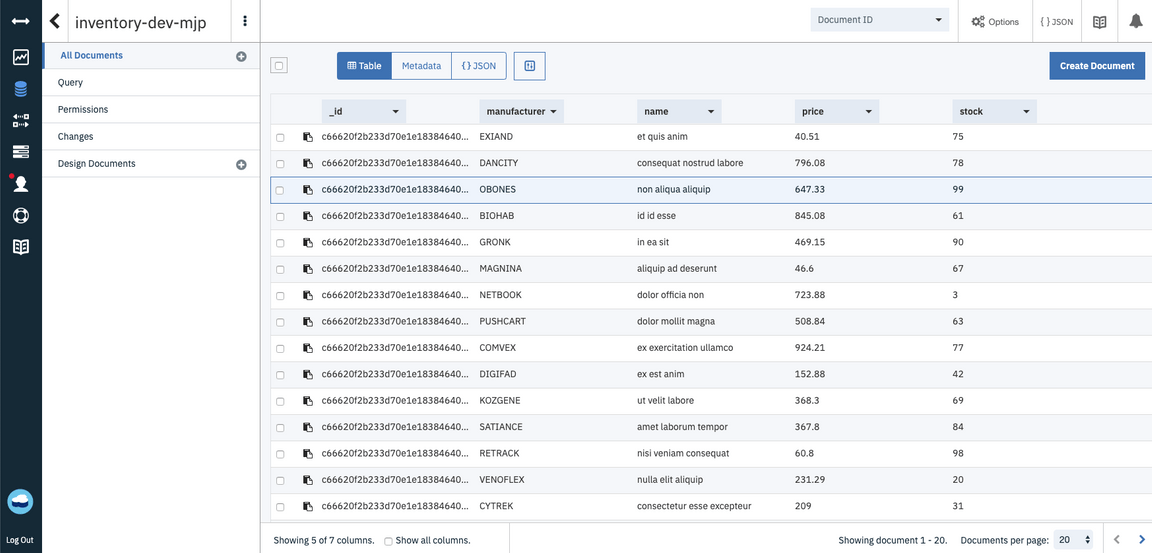
If you click on a row of data, you will see the raw NoSQL form of the data record.
This completes the setup of the database and populating it with data.
Enable database in the solution
If you are starting from the solution, use the following steps to enable the Cloudant database
Set up local development
Open the mappings.json file under src/main/resources and add a
DATABASE_NAMEvalue with the valueinventory-{namespace}wherenamespaceis the namespace where the pipeline is running (e.g. dev-{initials})src/main/resources/mappings.json{"DATABASE_NAME": "inventory-{namespace}"}Log into cloud.ibm.com and open the Cloudant service from the resource list
Click on service credentials and expand the listed credentials
Copy the json contents from the credentials into
mappings.jsonunder theCLOUDANT_CONFIGobject (note that CLOUDANT_CONFIG value must be a string type not a json type, so you must use escaping characters for this value)src/main/resources/mappings.json{"DATABASE_NAME": "inventory-{namespace}","CLOUDANT_CONFIG": "{paste json here}"}
Activate the Clouant service implementation
Open
src/main/java/com/ibm/inventory_management/services/StockItemMockService.javaand remove the@Profile("mock")annotationOpen
src/main/java/com/ibm/inventory_management/services/StockItemService.javaand add the@Primaryannotation. The file should look like the followingsrc/main/java/com/ibm/inventory_management/services/StockItemService.javapackage com.ibm.inventory_management.services;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Lazy;...@Service@Primarypublic class StockItemService implements StockItemApi {
Update the configuration values in the values.yaml helm chart
Open the
values.yamlfile and update the values forcloudantBindinganddatabaseNamechart/template-java-spring/values.yamlcloudantBinding="{binding name}"databaseName="inventory-{namespace}"Note: The cloudantBinding value should match the name of the cloudant binding secret
Add a Cloudant integration to your backend service
If you are following the instructions from MicroApp part 1 and want to enable the Cloudant database yourself, use the following directions.
Update the gradle config to include cloudant dependencies
- Enable the cloudant libraries by applying the
build-cloudant.gradleto the end of the build.gradle file
build.gradleapply from: 'gradle/build-cloudant.gradle'
- Run
./gradlew initto validate the changes and load the libraries
Configuration values
CloudantConfig is added to hold the url, username, password, and databaseName values
In CloudantMapping,logic is implemented to load the configuration from the secret binding or local file .
Set up local development
- Open the mappings.json file under src/main/resources and add a
DATABASE_NAMEvalue with the valueinventory-{namespace}wherenamespaceis the namespace where the pipeline is running (e.g. dev-{initials})
src/main/resources/mappings.json{"DATABASE_NAME": "inventory-{namespace}"}
Log into cloud.ibm.com and open the Cloudant service from the resource list
Click on service credentials and expand the listed credentials
Copy the json contents from the credentials into
mappings.jsonunder theCLOUDANT_CONFIGobject
src/main/resources/mappings.json{"DATABASE_NAME": "inventory-{namespace}","CLOUDANT_CONFIG": "{paste json here}"}
Service Implementation
CloudantApi component is added to create the CloudantClient instance from the configuration
Open the
deployment.yamlfile and add environment variables that use those values to the top of the existingenvblock
chart/template-java-spring/templates/deployment.yamlenv:- name: CLOUDANT_CONFIGvalueFrom:secretKeyRef:name: {{ .Values.cloudantBinding | quote }}key: binding- name: DATABASE_NAMEvalue: {{ .Values.databaseName | quote }}