Overview
Get familiar with using the Cloud-Native Toolkit
Cloud-Native Toolkit objectives
There are a number of objectives behind providing the Cloud-Native Toolkit. The three main goals of the Toolkit are provided below:
1. Accelerate time to business value
One goal of the Cloud-Native Toolkit is to prepare the development environment quickly and allow the development team to start delivering business function on day one of the first iteration using enterprise cloud-native practices. After all, the point of cloud-native development is to deliver business value to end users and the development and operations infrastructure are provided in service to that goal.
Through the automation provided by the Cloud-Native Toolkit we can provision an environment in minutes through automation that is fully configured and ready for a development team to start working immediately. With the other components of the Toolkit, developers can begin with a rich DevOps framework with a focus on “build to manage” techniques to help build production-ready applications.
2. Reduce risk through consistent delivery models from start to production
The Cloud-Native Toolkit encapsulates many of the available best practices for cloud-native development including DevOps and “Build to Manage” practices. They have been provided through the Toolkit in this way so that developers and SREs can benefit from these practices without requiring any additional effort and so that they can be applied consistently from project to project.
3. Quickly ramp up development teams on Red Hat OpenShift and Kubernetes
Containerized platforms like Red Hat OpenShift and Kubernetes provide a great deal of functionality and flexibility for application teams. However, these platforms can at time seem unapproachable for developers and SREs new to the environment given all the different concepts and components. The Cloud-Native Toolkit aims to help with the learning curve in two different ways:
- Provide tools and techniques to “round off the corners” of the more complex aspects of working in a containerized environment
- Provide a learning journey that incrementally introduces the concepts of a containerized environment in terms of practical scenarios, not abstract theory
Guided walk-though
If you’d like to have a guided walkthrough of what the Cloud-Native Toolkit provides, check out this video demonstration of the Toolkit in action.
Components of the Cloud-Native Toolkit
As the name suggests, the Cloud-Native Toolkit provides a collection of tools that can be used in part or in whole to support the activities of software development life-cycle. The following provides a listing of the assets that make up the Cloud-Native Toolkit:
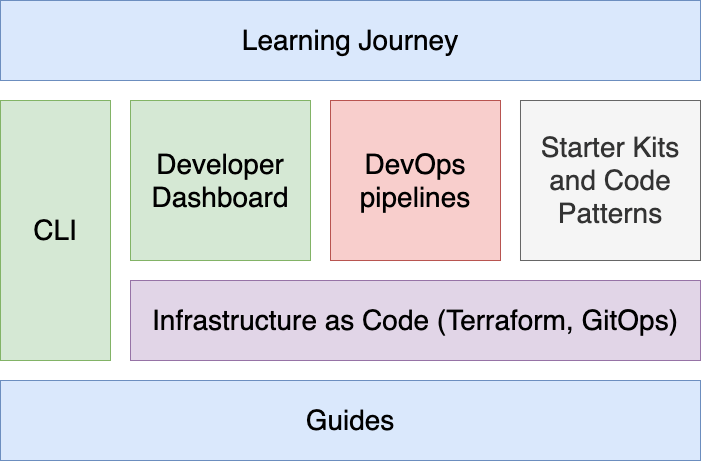
- Guides - this set of documentation that weaves the various toolkit components together with a perspective on how to apply cloud-native practices to deliver business solutions
- Infrastucture as Code - Terraform scripts and GitOps configuration to provision and manage the environment
- CLI - a simple node-based CLI that installs as a plugin to the
kubectlandocCLIs and provides commands to simplify common - Developer Dashboard - Dashboard component and Red Hat OpenShift console extensions to simplify common developer activities
- DevOps pipelines - continuous integration pipelines for Tekton and Jenkins
- Starter Kits and Code Patterns - software repositories that can be used to quickly get started building applications using common patterns, or to serve as a reference to enhance existing patterns
- Learning Journey - activation material to teach practitioners how to apply cloud-native practices in real-world scenarios using the Toolkit
Cloud-Native Toolkit Developer Environment
The Cloud-Native Toolkit Developer Environment includes several features that support IBM Garage Method best practices for consistent and rapid development of cloud-native applications:
- Cluster: A Red Hat OpenShift or Kubernetes cluster that both hosts the tools and itself is a deployment target for application builds
- SDLC: Deployment target environments that support the application development lifecycle: dev, test, and staging
- Backend services: Cloud services commonly required by cloud-native applications for monitoring, security, and persistence
- CI/CD: A prebuilt, ready-to-run continuous delivery pipeline incorporating best-of-breed open source software tools
- Starter Kits: Prebuilt code templates for common application components and tasks incorporating best practices that developers can add to their codebase as needed
- Dashboard: A centralized console to help developers use the environment’s capabilities
Typically a Cloud System Admin (or a squad lead) installs and sets up a new Developer Environment after the inception workshop, providing a place for the developers to start developing the minimum viable product (MVP). The objective is to reduce the time required for a team to configure and prepare their development environment. The key benefit is to make the end-to-end CI/CD development lifecycle consistent across each platform and make the out-of-the-box developer experience as simple as possible.
The installation is performed using Terraform scripts structured as modular components so unneeded tools can be easily disabled or new tools added. The combination of tools selected are proven in the industry to deliver real value for modern cloud-native development.
Red Hat Open Innovation Labs CI/CD components embodies a very similar approach to how they deliver success with OpenShift.
Environment components
After installation, the environment consists of the following components and developer tools:
- A Red Hat OpenShift or IBM Cloud Kubernetes Service development cluster
- A collection of continuous delivery tools deployed into the cluster
- A set of backend services
This diagram illustrates the environment:
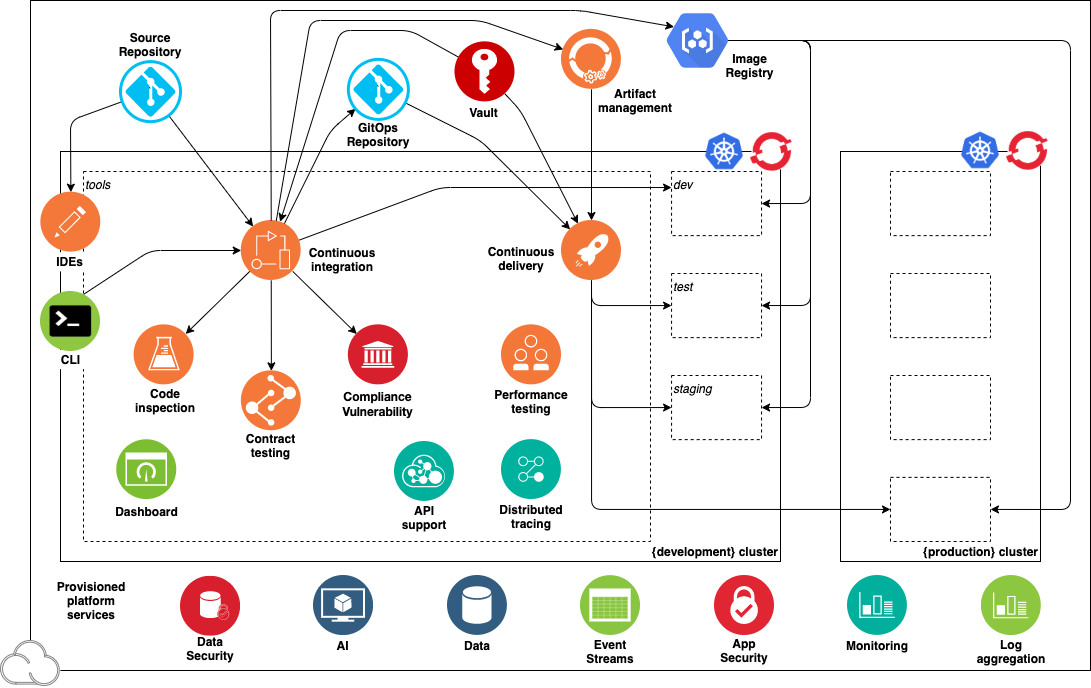

The diagram shows the components in the environment: the cluster, the deployment target environments, the cloud services, and the tools.
Logo Usage Reference Artifactory is an Open Source product maintained by JFrog Jenkins Open Source project Jenkins SonarQube Open Source project maintained by SonarSource Nexus Repository Open Source project maintained by SonaType Trivy Open Source project maintained by Aqua InteliJ IDE from JetBrains VSCode Free IDE maintained by Microsoft Jaeger Open Source tool maintained by Jaeger Community ArgoCD Open Source tool maintained by ArgoCD Community OpenShift and CodeReady Workspaces are products from Red Hat LogDNA IBM Cloud service supplied by LogDNA Sysdig IBM Cloud service supplied by Sysdig
The tools to provision an environment using the Cloud-Native Toolkit can the customized to provision a particular set of tools fit for the environment. The Toolkit provides a default installation to provision a Developer Environment as a starting point. Any of the available components listed on the Terraform modules page can be used to prepare the environment.
Development cluster
The heart of the Developer Environment is a cluster:
- An IBM Cloud-managed Kubernetes or Red Hat OpenShift cluster
- Cluster namespace that encapsulates the tooling installed in the cluster: tools
- A collection of SRE tools and services
Continuous delivery tools
The following best-of-breed open source software tools are installed in the cluster’s tools namespace:
| Capability | Tool | Bitnami | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous Integration | Jenkins CI | Yes | Jenkins is a common tool for Continuous Integration |
| Continuous Integration | Tekton CI | Tekton is an emerging tool for Continuous Integration with Kubernetes and OpenShift | |
| API Contract Testing | Pact | Pact enables API contract testing | |
| Code Analysis | SonarQube | Yes | SonarQube can scan code and display the results in a dashboard |
| Container Image Registry | IBM Cloud Container Registry | Stores container images to be deployed | |
| Artifact Management | Artifactory | Yes | Artifactory is an artifact storage and Helm chart repository |
| Continuous Delivery | ArgoCD | ArgoCD support Continuous Delivery with GitOps | |
| Web IDE | Code Ready Workspace | IDE for editing and managing code in a web browser |
Backend services
The following services can be created and bound to the cluster:
| Capability | Service | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Log Management | Log Analysis with LogDNA | Manage and analyze app logs |
| Monitoring | Cloud Monitoring with Sysdig | Monitor app and platform resources |
| User Authentication | App ID | Verify identities of clients accessing app end points |
| Relational Data Storage | Databases For PostgreSQL | Stores relational data structured as schemas for SQL querying |
| Schemaless Data Storage | Cloudant | NoSQL database for JSON documents |
| Binary Data Storage | Cloud Object Storage | Storage service commonly used for binary content |
Getting Started
Get to know the Cloud-Native Toolkit: