Infrastructure as Code Terraform
Overview
Infrastructure as Code is the practice of defining and managing the logic used to provision infrastructure as versioned
artifacts in the same way that code artifacts have traditionally been handled. There are a number of different tools and
frameworks available that enable this type of approach. The IBM Garage for Cloud Developer Tools currently leverage
Terraform as the technology used to implement the Infrastructure as Code strategy.
The IasC terraform logic is stored in two repositories:
garage-terraform-modulesThe modules that provide logic to provision individual components of the infrastructure. These modules cover one of three different categories: infrastructure (e.g. create a kubernetes cluster), cloud service, or software deployed and configured into a cluster. https://github.com/cloud-native-toolkit/garage-terraform-modules
ibm-garage-iteration-zeroThe logic that makes use of the modules with specific configuration parameters used to deliver an entire solution. https://github.com/cloud-native-toolkit/ibm-garage-iteration-zero
This guide will walk through the various files that make up the Infrastructure as Code components and how to customize them. The Installation Overview walks through how to perform an install with the Iteration Zero scripts.
Iteration Zero terraform scripts
The Iteration Zero terraform scripts make use of the modules to provision and prepare an environment. The logic is
provided as stages that can be removed and added as needed.
Stages
The files in the stages and stages-crc folders provide Terraform files that make use of external
Terraform modules to provision resources. The different resources are logically grouped with stage numbers
and names for the resource provided. All of the stages are processed by the Terraform apply at the same
time and Terraform works out the sequencing of execution based on the dependencies between the modules.
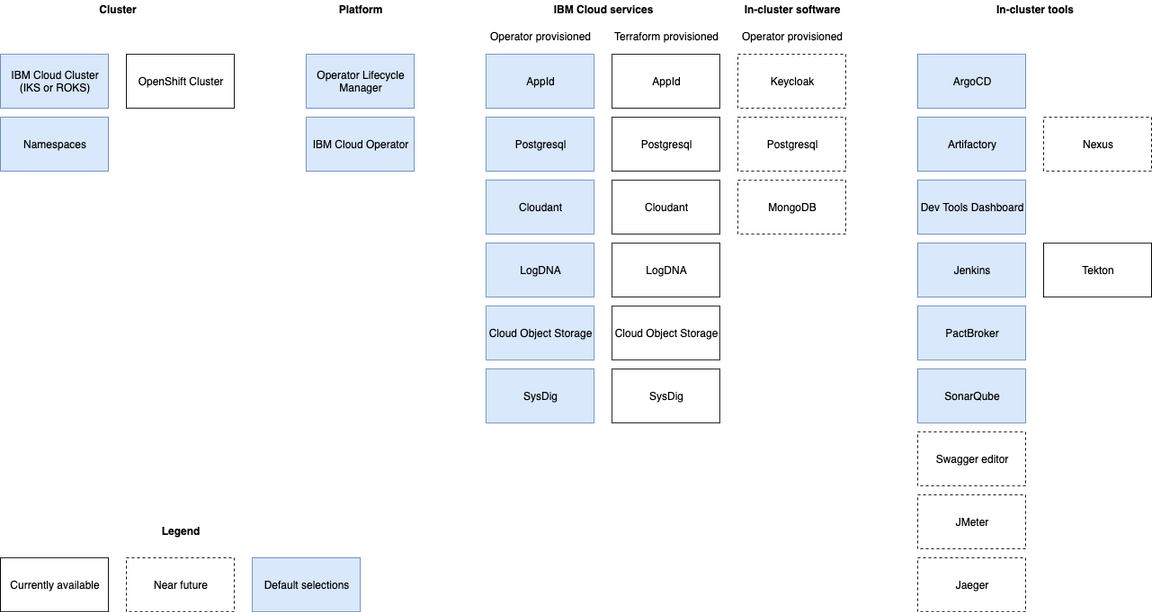
The Iteration Zero application comes with a pre-defined set of software and services that will be provisioned. For more advanced situations, that set of modules can be easily customized.
Removing a stage
To remove a stage, simply delete or move a file out of the stages directory
Adding a stage
To add a stage, define a new stage file and reference the desired module. Any necessary variables can be referenced from the base variables or the output from the other modules.
Modifying a stage
Any of the values for the variables in
variables.tfor in the stage files can be updated to change the results of what is built
Environment configuration
There a number of files used to provide the overall configuration for the environment that will be provisioned.
credentials.templateTemplate file for the credentials.properties
credentials.propertiesFile containing the API key and Classic Infrastructure credentials needed to run the scripts
terraform/settings/environment.tfvarsGeneral configuration values for the environment, like
region,resource groupandcluster typeterraform/settings/vlan.tfvarsConfiguration values for the IBM Cloud vlan settings needed for the creation of a new cluster
terraform/stages/variables.tforterraform/stages-crc/variables.tfDefined variables for the various stages and, in some cases, default values.
Scripts
launch.shLaunches a container image from the Docker Hub registry that contains all the tools necessary to run the terraform scripts and opens into a shell where the Terraform logic can be run
terraform/runTerraform.shBased on the values configured in
environment.tfvars, this script creates theterraform/workspacedirectory, copies the appropriate Terraform files into that directory, then applies the Terraform scriptsterraform/scripts/apply.shApplies the Terraform scripts. This script is copied into the
terraform/workspacedirectory during therunTerraform.shlogic. It is then available to rerun the Terraform logic without having to set theterraform/workspacedirectory up again.terraform/scripts/destroy-cluster.shHelper script that destroys the IBM Cloud cluster to clean up the environment
terraform/scripts/destroy-services.shHelper script that destroys services that have been provisioned in IBM Cloud. It works against the
resource groupthat has been configured in theenvironment.tfvarsfile. Any values passed in as arguments will be used to do a regular expression match to exclude services from the list of those that will be destroyed.
Garage Terraform Modules
The terraform modules project contains the building block components that can be used to create a provisioned environment. The modules are organized into one of three major categories:
cloud-managedModules that provision infrastructure (cluster and/or services) into a managed cloud environment
self-managedModules that provision infrastructure into a self-managed environment (e.g. software deployed into a cluster)
genericModules that can be applied independent of the environment (e.g. software that is installed into a running kubernetes environment)
A listing of the modules is shown below: